
Recently, visa-free travel has gained significant traction, marking a transformative shift in global tourism. Driven by post-pandemic recovery efforts, globalization, and stronger diplomatic ties, this trend holds particular importance for the halal travel segment. The Global Muslim Travel Index (GMTI) 2024 highlights visa-free policies as key to attracting Muslim travelers by simplifying access and enhancing destination appeal, making them a crucial driver of growth in Muslim-friendly tourism.
Visa-free travel minimizes bureaucratic hurdles, making destinations more attractive to tourists. The United Nations World Tourism Organization (UNWTO) reported 1.3 billion international tourist arrivals in 2023, a testament to the trend's success. Destinations that simplify access witness a tangible increase in footfalls, benefiting local businesses and economies.
For Muslim travelers, visa-free policies simplify the planning process, aligning with their preference for seamless experiences. Destinations like Malaysia and Indonesia, which extend visa-free access to many countries, are reaping these benefits.
The correlation between visa-free access and economic upliftment is undeniable. Indonesia’s 30-day visa waiver policy between 2015 and 2018 catalyzed a 24% rise in inbound tourism, creating 190,000 jobs. Similarly, studies indicate that visa-free arrangements can bolster cross-border trade, further enhancing economic cooperation.
For halal tourism, this means increased opportunities for destinations to attract Muslim travelers, a segment known for its substantial economic impact.
Visa-free policies often reflect and reinforce geopolitical alliances. For example, Turkey's 2016 agreement with the EU aimed to facilitate visa-free travel for Turkish citizens, illustrating how such measures foster goodwill and collaboration.
The Organization of Islamic Cooperation (OIC), with its 57 member states, showcases a complex landscape of visa policies. While some nations promote seamless travel within the bloc, others maintain restrictive entry requirements.
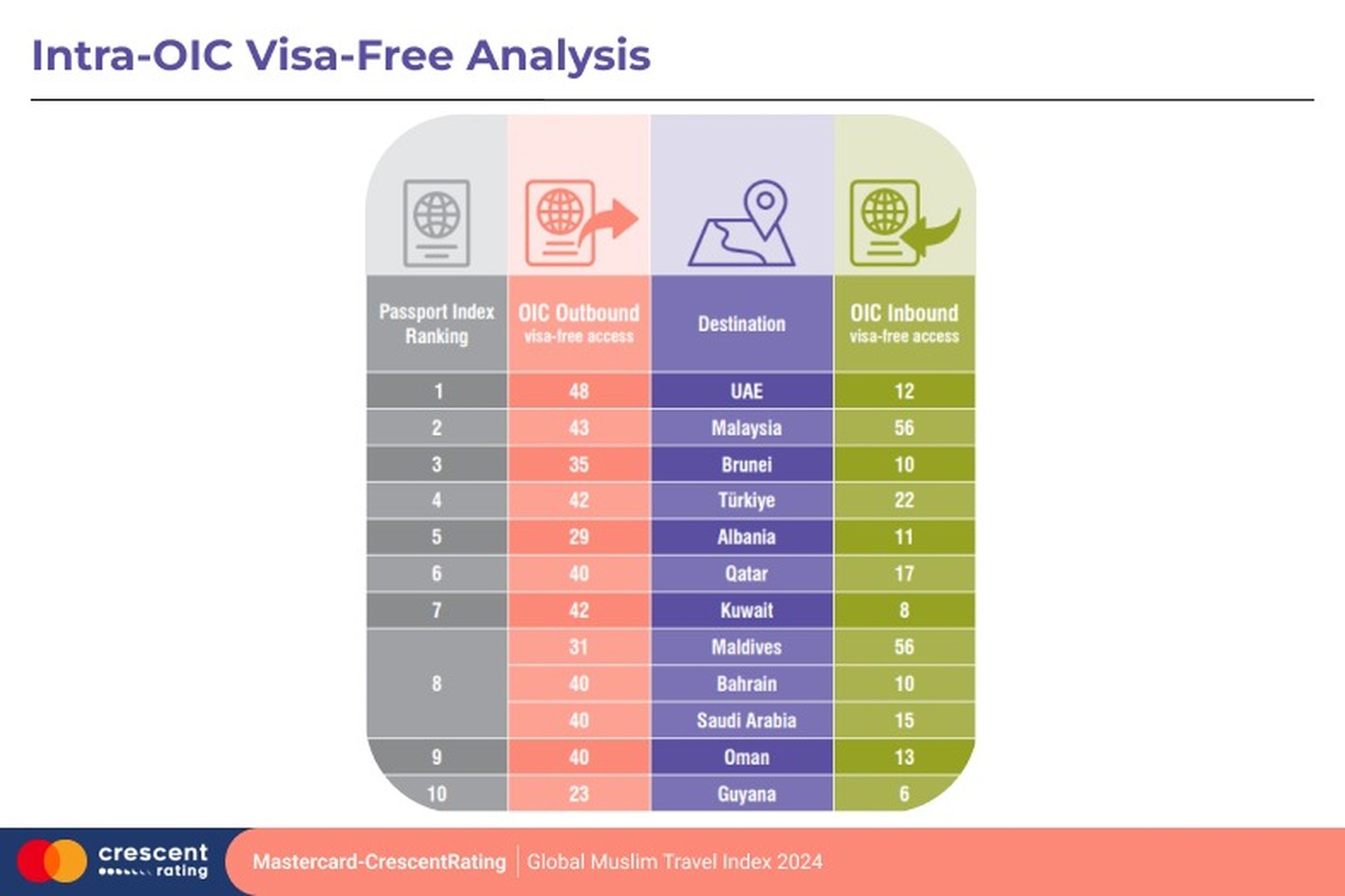
Despite sharing common values and a collective vision for greater cooperation, OIC countries exhibit significant disparities in their visa-free access policies. Malaysia and the Maldives lead as some of the most open nations, granting visa-free entry to most OIC destinations, reflecting their commitment to fostering regional connectivity and economic ties. In contrast, Indonesia adopts a more selective approach, offering visa-free access to only 15 OIC member states. This underscores its cautious stance, likely driven by specific security considerations and strategic economic priorities. These variations highlight the diverse national agendas and priorities across OIC countries, influenced by economic objectives, geopolitical strategies, and the need to address domestic security concerns.
The Gulf Cooperation Council (GCC) exemplifies intra-regional mobility through its free movement policy among member states using national IDs. This arrangement has enhanced economic productivity and could serve as a blueprint for broader OIC cooperation.
Visa-free access within the OIC significantly drives tourism inflows, showcasing the potential of fostering greater mobility among member states. Malaysia and Indonesia exemplify this trend, with approximately 20% of their inbound tourists originating from OIC countries, reflecting the value of regional openness in attracting Muslim travelers. Similarly, despite maintaining limited visa-free policies, Egypt draws 30% of its tourists from within the OIC. This underscores the latent potential of the market and highlights how even a partial easing of travel restrictions can create substantial opportunities for tourism growth and economic collaboration among member states.
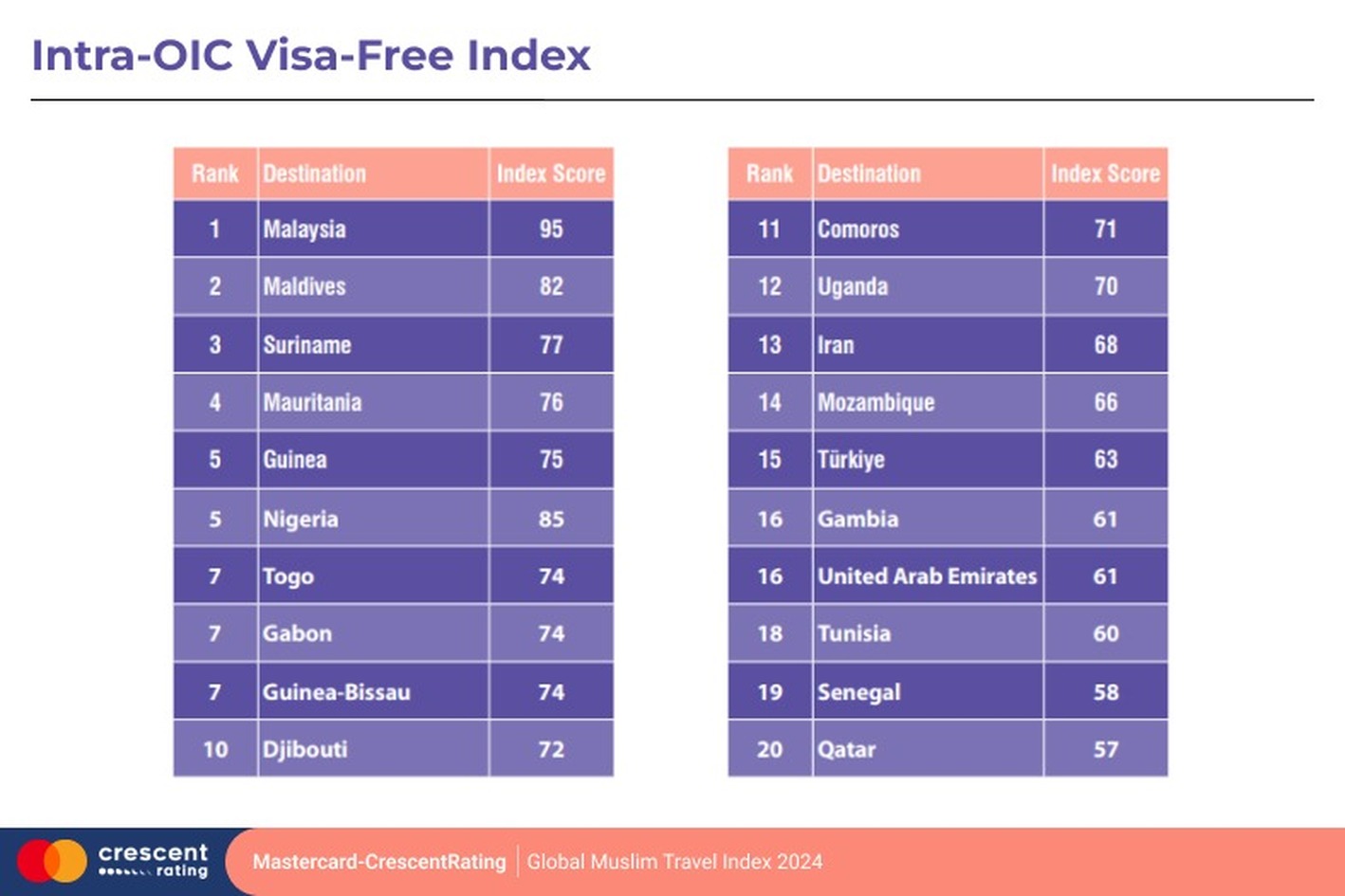
The Intra-OIC Visa-Free Index is a benchmark for assessing travel freedom within the OIC, assigning a score out of 100 to evaluate member states' openness level. Malaysia stands out as a leader with a high score of 95, showcasing its strong commitment to fostering Muslim travel and promoting seamless mobility within the region. In contrast, despite their global reputation for high mobility, the UAE and Qatar rank lower on the index due to their more restrictive intra-OIC visa policies. This disparity highlights the need for greater collaboration and alignment among OIC nations to enhance regional connectivity.
For destinations aiming to attract Muslim travelers, visa-free policies present both opportunities and responsibilities.
Destinations must balance openness, sustainability, and security to maximize the benefits of visa-free travel. Customizing visa-free agreements based on economic and cultural compatibility is essential, focusing on prioritizing key markets. Additionally, deploying advanced monitoring systems helps track visitor activities and prevent potential abuses, ensuring safe and seamless travel experiences. Engaging industry stakeholders, such as airlines and travel agencies, can promote smoother travel processes while preserving local cultures and heritage. By integrating responsible tourism practices into visa-free policies, destinations can maintain authenticity while accommodating growing tourism numbers.
Visa-free travel is more than just a policy; it catalyzes transformation in global tourism. For halal-friendly destinations, embracing this trend can unlock unprecedented opportunities to engage Muslim travelers. As the halal tourism industry evolves, strategic visa policies, informed by data-driven insights, will be key to achieving sustainable growth and fostering cross-cultural connections.
Visit the CrescentRating Insights Vol 2 publication for more insights on Visa-free travel!